The sense of sight let us see colours, shapes, sizes, brightness and distances. We need light in order to see the objects. EyesEyes are the organs for sight. Eyes have different parts:
 |
- The parts responsible for vision:
- The iris is the coloured part of the eye. It controls the amount of light that enters the eye.
- The pupil is in the center of the iris. Light enters through the pupil to the inside of the eye.
- The lens is inside the eye. It is behind the pupil and the iris. It also helps us to see objects in focus.
- The retina is at the back of the eye. The light entering the eye travels until it reaches the retina. The optic nerve is attached to the retina.
How does the sense of sight work? How do we see?
Light enter the eye through the pupil. It travels through the lens; the lens focuses the objects we see.
When the light reaches the retina, it percieves different sensations: colour, shape and size.
This information goes to the optic nerve. This nerve carries the information to the brain.








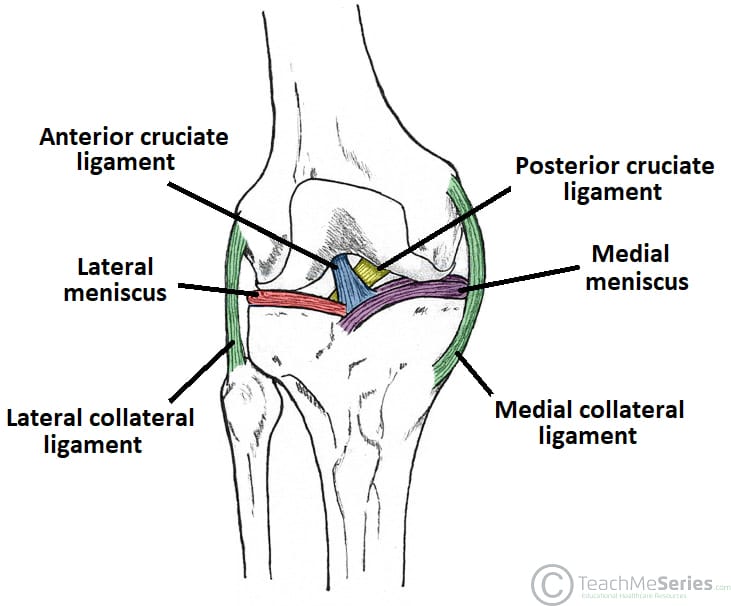

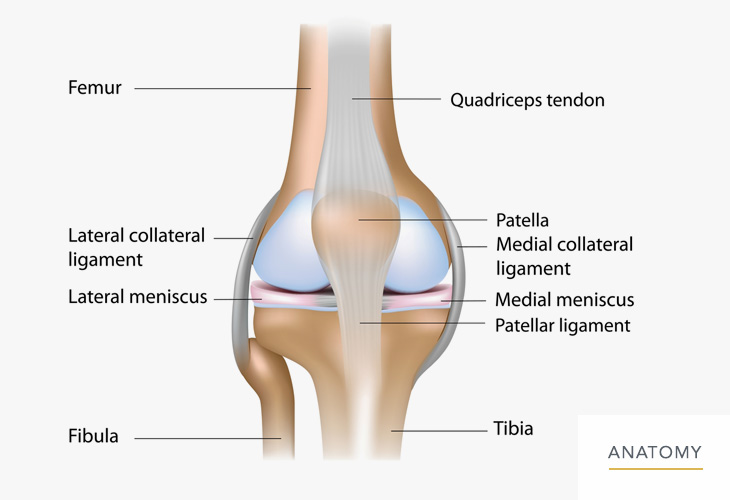

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/vector-illustration-of-a-meniscus-tear-and-surgery-871162428-03ac23d73f854954a8082f2ae3ce9219.jpg)